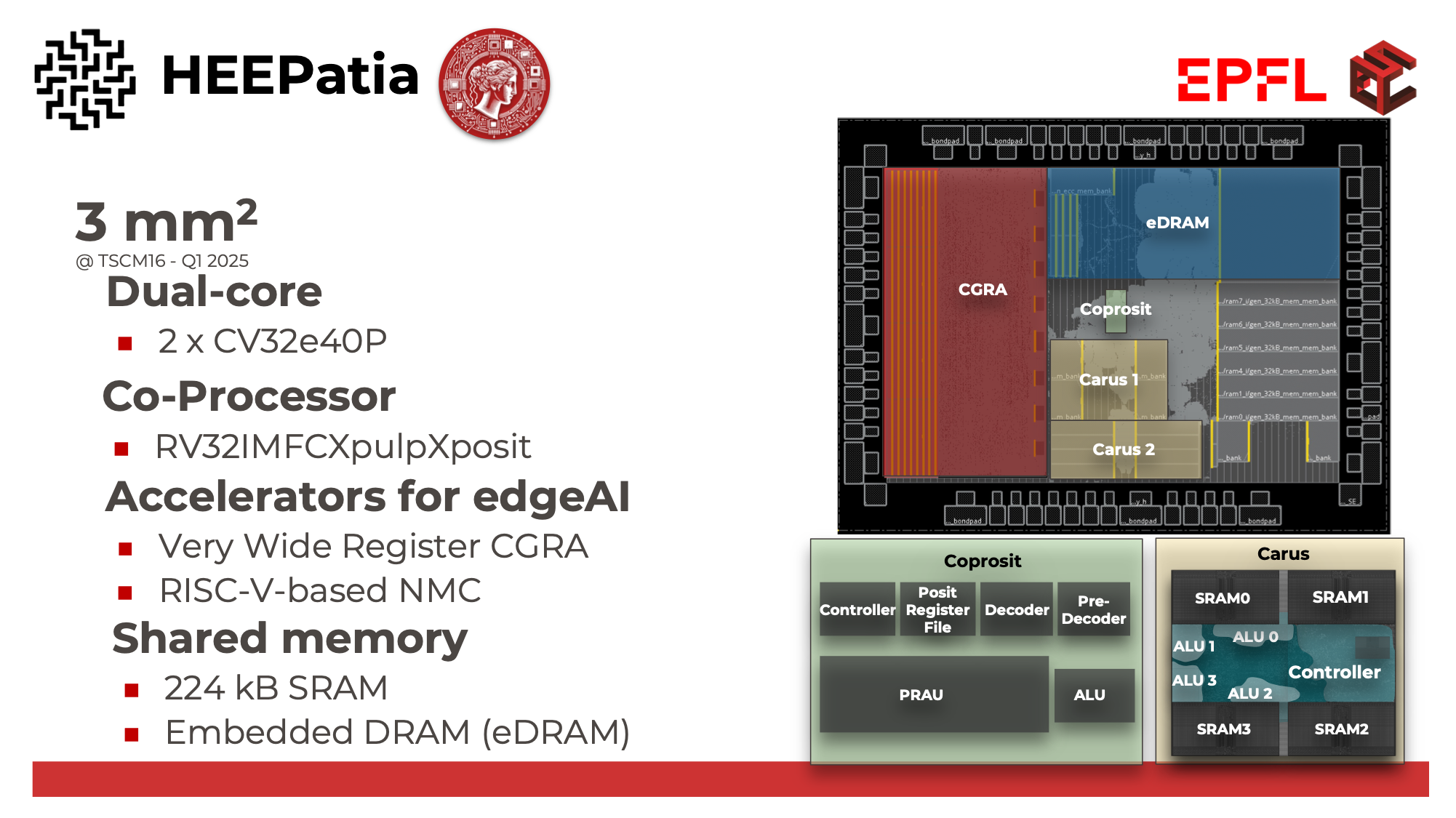
WP6: Chips for Edge AI
WP6 will develop highly efficient IC solutions that implement a large part of the artificial intelligence (AI) workload “at the edge,” i.e., on the device, locally, and without the need for cloud access. Chip solutions for such edge-AI applications will be developed to efficiently accelerate a wide range of machine learning and inference tasks for applications ranging from cameras to industrial IoT systems and medical devices.
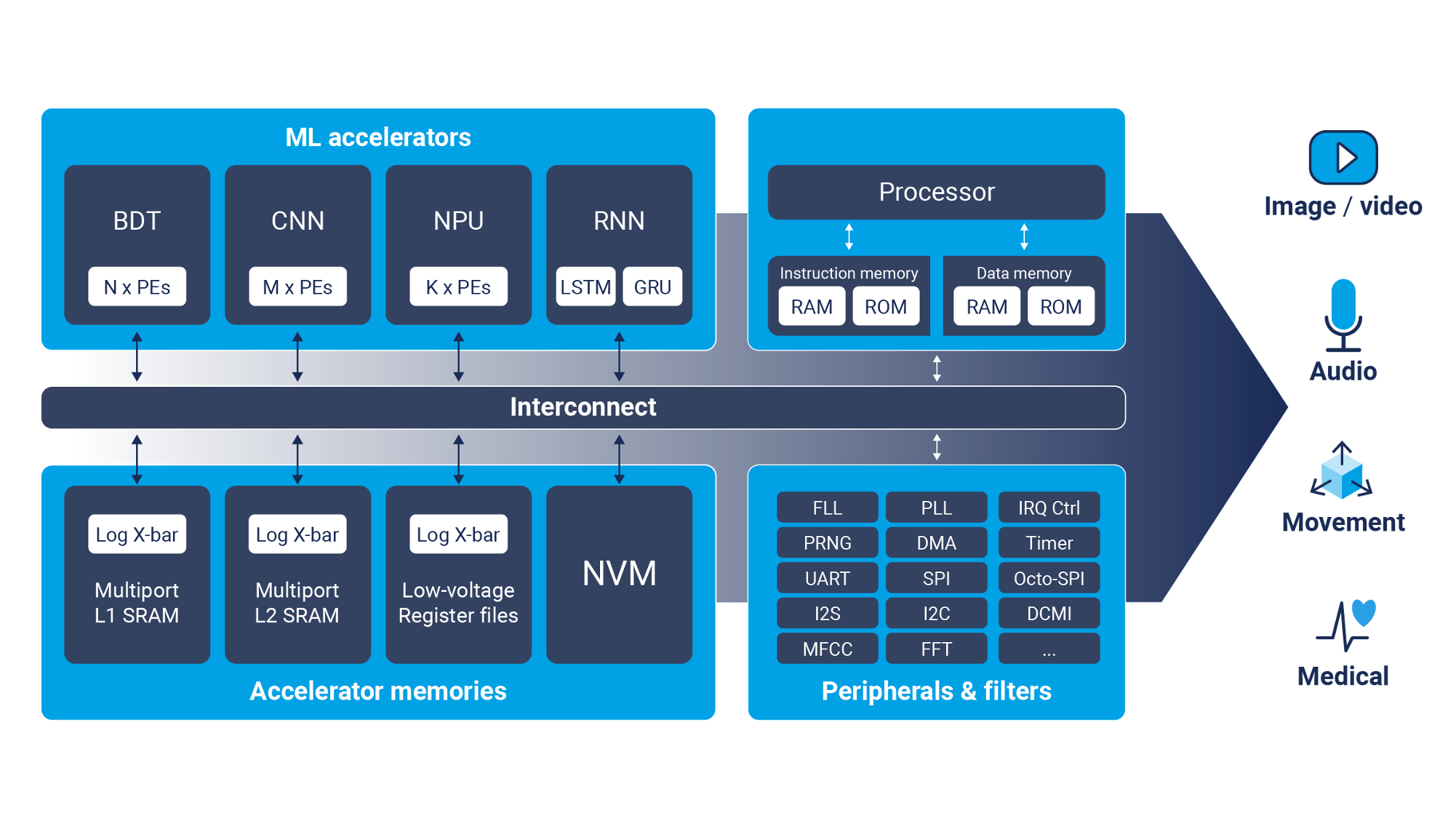
The main goals of this WP are to develop highly efficient integrated circuits which will perform a large part of the artificial intelligence (AI) workload “at the edge”. Chips for edge AI contain custom-designed (co-)processors optimized for AI tasks and are integrated into edge devices. These chips are also known as AI accelerators or neural processing units (NPUs). Such specialized chips are designed to efficiently run AI algorithms, such as deep learning models, using low power and small area, making them suitable for use in a wide range of edge devices, from cameras to industrial IoT systems and medical devices. In the realm of IoT, edge AI empowers devices to process data locally, enabling quicker responses and reduced data transfer, thus enhancing overall system efficiency and responsiveness. Likewise in the healthcare sector, edge AI plays a pivotal role by enabling real-time diagnostics, personalized treatments, and closed-loop interventions through localized AI processing. This technology aligns strategically with the European Commission's goals, in particular with Horizon Europe and the scope of fundamental research promoted by the European Research Council in the areas of adaptive medical devices and wearables as well as autonomous devices for Industry 4.0. Therefore, this WP targets to fortify the innovation and creation of Switzerland within Europe's technological leadership in this edge AI domain. This highly dynamic field of research is of great strategic importance internationally and through this WP, Switzerland can enhance many collaborations already happening within European research and with industrial partners in order to secure and further develop its position in this domain.
WP6 Lead: Dr. Stéphane Emery, CSEM
Stéphane Emery leads the SoC (System on Chip) & Mixed Signal Design group at external page CSEM in Zürich. The group focuses on the design of low-power integrated circuits (ASIC).
Contact: external page Stéphane Emery,
WP6 Co-lead: Prof. David Atienza (EPFL)
David Atienza leads the external page Embedded Systems Laboratory (ESL), part of the external page Institute of Electrical and Micro Engineering at external page EPFL. The group focuses on the definition of system-level multi-objective design methods, optimization methodologies and tools for high-performance embedded systems and nano-scale Multi-Processor System-on-Chip (MPSoC) architectures targeting the Internet-of-Things (IoT) Era.
Contact: external page David Atienza
WP6 Task Leaders & Senior Collaborators
WP6 Students, Postdocs & Affiliated Researchers
- external page Lara Orlandic, PhD student, Supervisor: Prof. David Atienza
- external page Simone Machetti, PhD student, Supervisor: Prof. David Atienza
- external page Dr. David Mallasen Quintana, Postdoc, Supervisor: Prof. David Atienza
- Victor Jung, PhD student, ETH
- Cristian Cioflan, PhD student, ETH
- external page Dr. Davide Schiavone, Postdoc, EPFL, Supervisor: Prof. David Atienza
- external page Huanshihong Deng, PhD student, EPFL, Supervisor: Prof. Mahsa Shoaran
- external page Nazareno Sacchi, PhD student, CSEM, Supervisor: Dr. Stéphane Emery
- external page Jan Snoeijs, PhD student, CSEM, Supervisor: Dr. Stéphane Emery
- Daniel Keller, PhD student, CSEM, Supervisor: Dr. Stéphane Emery